
Singapore unveiled a new framework to assess Employment Pass applications called COMPASS, this article is a full guide on how to navigate these new requirements.
- The objectives of the New COMPASS Framework
- How COMPASS works
- Exemptions to COMPASS Requirements
- Further documentation for EP Application
- Points to consider before getting an Employment Pass
The objectives of the New COMPASS Framework
The Ministry of Manpower (MoM) announced on March 4th 2022 a new update to immigration policy. In line with Singapore’s objective to develop skills and employment of Singaporeans and Permanent residents, the new policy will also bring more clarity and higher certainty to businesses in regard to their employment visa matters. The MoM communicated that the goal remains the same and is to ensure that foreign workers’ visas are attributed to fill in the gap from local workforce rather than save on costs.
Starting on September 1st 2023, the new Employment Pass (EP) applicants will have to go through the Complementary Assessment Framework (COMPASS). EP renewals will also have to be eligible through the COMPASS framework from September 1st of 2024.
For all EP applications the qualifying salary will still apply, and, as a reminder: for all sectors, and from September 1st of 2022 onwards, the minimum qualifying salary for an EP will be S$ 5,000 per month. In the financial sector, the minimum qualifying salary will be raised to S$ 5,500 per month.
How COMPASS works
The new COMPASS framework comes in addition to the qualifying salary and consist of a point-based system to assess eligibility to the Employment Pass. Based on 6 criteria the scoring systems awards 0, 10 and 20 points per criterion, respectively corresponding to “does not meet expectations”, “Meet expectations” and “Exceeds expectations”.
An EP applicant needs a total of 40 points or more to be eligible for the Employment Pass.
| Total Points | Application eligibility |
|---|---|
| 40 and more | Yes |
| Less than 40 | No |
Points per criterion and their actual assessment under COMPASS framework
| Points per criterion | Assessment |
|---|---|
| 20 | Exceeds expectations |
| 10 | Meets expectations |
| 0 | Below expectations |
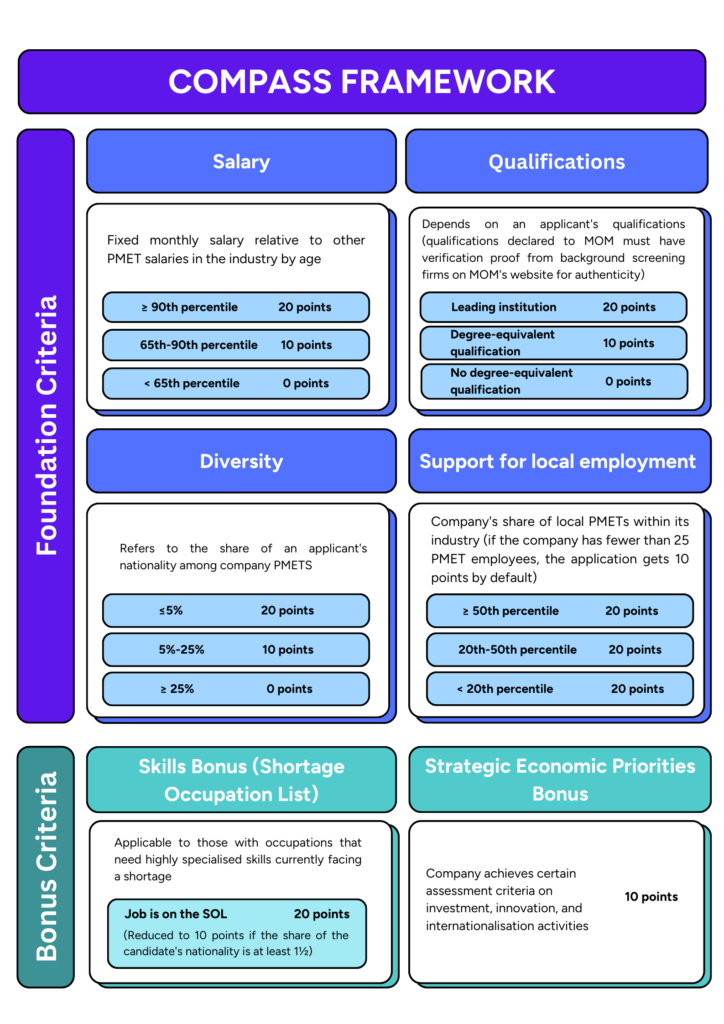
None of the criteria can lead to disqualification but a total number of points below 40 will not be sufficient to be eligible to the EP.
Each criterion has been designed to ensure fairness and non-discrimination towards local applicants:
- Salary criterion: The applicant’s salary will be compared to the salaries of current employees of the same sector and similar age. Salary benchmarks per sector are available on the MOM website to better guide employers on their applicants ranking. You can find this guide on the following link by the MOM.
- Qualification criterion: The applicant’s academic qualifications will be measured based on: the world top 100 ranking universities, Singaporean Universities and highly recognized vocational institutions. In terms of degree-equivalent qualifications, the standard comparison will be a United Kingdom academic system bachelor’s degree. Qualifications will also have to be verified by the employer. You can find the list of top-tier institutions on the MOM website.
- Diversity criterion: The percentage of PMET employees from the nationality of the applicant relative to the number of firm’s PMET will be required to assess this criterion. For example, if the number of PMETs of the same nationality than the applicant in the company is high, then the applicant is less likely to score points on the diversity criterion.
- Support of local employment: The percentage of local (meaning Singaporean or Permanent Residents) PMET employees will be compared to other companies within the same industry / sector. Employers with a higher share of local employees than other peer companies from the same sector will score points on this criterion.
- Shortage Occupation List: Talents on shortage on the local job market might be reflected within the Shortage Occupation List, as such, applications to fill a job listed will score extra points.
- Strategic Economic Priorities: Applications from companies undertaking innovative and international activities in partnership with the Singaporean government will score extra points.
Exemptions to COMPASS Requirements
Some exemptions will also be possible from the COMPASS framework of New Employment Pass for applicants fulfilling at least 1 of the following conditions to be eligible to Employment Pass in Singapore:
- Applicant’s fixed monthly salary will be at least SGD 22,500. The candidate is exempted from both COMPASS and the salary eligibility requirements.
- Applicant is an overseas intra-corporate transferee under the WTO General Agreement on Trade in Services or an applicable Free Trade Agreement with Singapore.
- Applicant’s role is for 1 month or less.
Further documentation for EP Application
To clarify the process, some further documentations have been published by the Singaporean government:
- The Indicative Sectoral Salary Benchmarks (relative to the Salary criterion) is available on the MOM portal of Employment Pass eService
- The Company’s performance on firm-related attributes (relative to the Diversity and Support for Local Employment criteria) is also available on the MOM portal of Employment Pass eService
- The Occupations on the shortage occupation list (relative to the Shortage occupation list criterion) is available on the MOM’s website
- More information about the Programmes and eligibility criteria for the Strategic Economic Priorities criterion is detailed on the MOM’s web page
- A Pre-assessment tool to have an indicative outcome of the COMPASS is available on the MOM portal of Employment Pass eService and allow to assess if a candidate will pass the COMPASS framework.
Points to consider before getting an Employment Pass
The New Employment Pass (EP) requirements of COMPASS still offer a very good opportunity to work and live in Singapore. The EP is mostly for foreign professionals, managers, executives, and specialists.
Advantages of the Employment Pass
- Access to job opportunities: The EP allows foreign professionals to work in Singapore and gain access to a wide range of job opportunities in various industries. Singapore has a thriving economy and is home to many multinational companies, which makes it an attractive destination for foreign workers.
- Competitive salaries: Singapore offers competitive salaries and benefits to foreign workers, which can help them improve their standard of living. In addition, the EP allows foreign workers to bring their families to Singapore under the Dependant Passes (DP), which can provide a better quality of life for them.
- Tax incentives: Foreign workers who hold an EP are subject to a progressive tax rate going from 2% to 24%, which is low in global comparison.
- Permanent residency (PR): Foreign workers who hold an EP for at least 6 months and meet other eligibility criteria may be eligible for permanent residency in Singapore.
Disadvantages of the EP
- High cost of living: Singapore has a high cost of living, and foreign workers may find it challenging to afford housing, healthcare, and other basic necessities. Singapore has been ranked one of the most expensive city for expatriates in 2022.
- Strict immigration policies: Singapore has strict immigration policies, and foreign workers may face difficulties obtaining an EP if they do not meet the eligibility criteria. The Employment Pass must be sponsored by the employer which will also handle the application process for the employee.
- Limited job security: EP holders are tied to their employers, and if they lose their job, they must find another employer to sponsor a new EP within a limited timeframe or risk losing their right to work in Singapore and thus have to depart.
- Limited social benefits: Foreign workers who hold an EP may not be eligible for the same social benefits as Singaporean citizens, such as subsidized healthcare and education. Although, it is possible to negotiate for some benefits with the employer to compensate for this.



